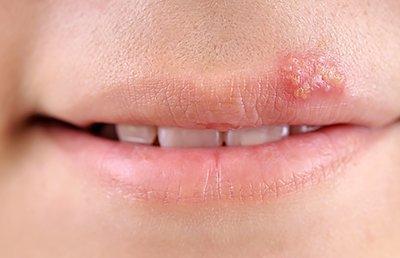
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). This is a common viral infection that affects many people worldwide.
Once a person is infected, the virus stays in the body and can reactivate due to stress, illness, or sun exposure. When triggered, it causes painful blisters, usually around the lips, but they can also appear on the nose, chin, or inside the mouth.

Effective Treatment Methods
Managing cold sores usually requires both medical treatments and lifestyle changes.
Antiviral medications like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir work best when taken at the first sign of symptoms. They help speed up healing and reduce the severity of outbreaks.
Over-the-counter treatments containing antiviral agents such as docosanol can also help. Additionally, topical numbing creams like lidocaine may relieve discomfort and prevent the sore from worsening if applied early.

Home Remedies for Cold Sores
In addition to medications, some home treatments can help manage symptoms and support healing.
Aloe vera gel is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can reduce discomfort and promote healing. Similarly, lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) has antiviral effects and may shorten the duration of outbreaks when applied as an ointment.
Using a cold compress can help ease pain and swelling. Applying diluted tea tree oil, which has antibacterial properties, may also support the healing process.
Preventing Future Outbreaks
To lower the risk of future cold sores, it’s important to identify and avoid personal triggers. These may include stress, sun exposure, hormonal changes, and certain foods like chocolate or nuts.
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular exercise, can strengthen the immune system. Getting enough rest and taking supplements like lysine may also help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Good hygiene is key. Washing hands often and avoiding touching the affected area can prevent the virus from spreading to others or to different parts of the body. Avoid sharing personal items to reduce the risk of transmission.

